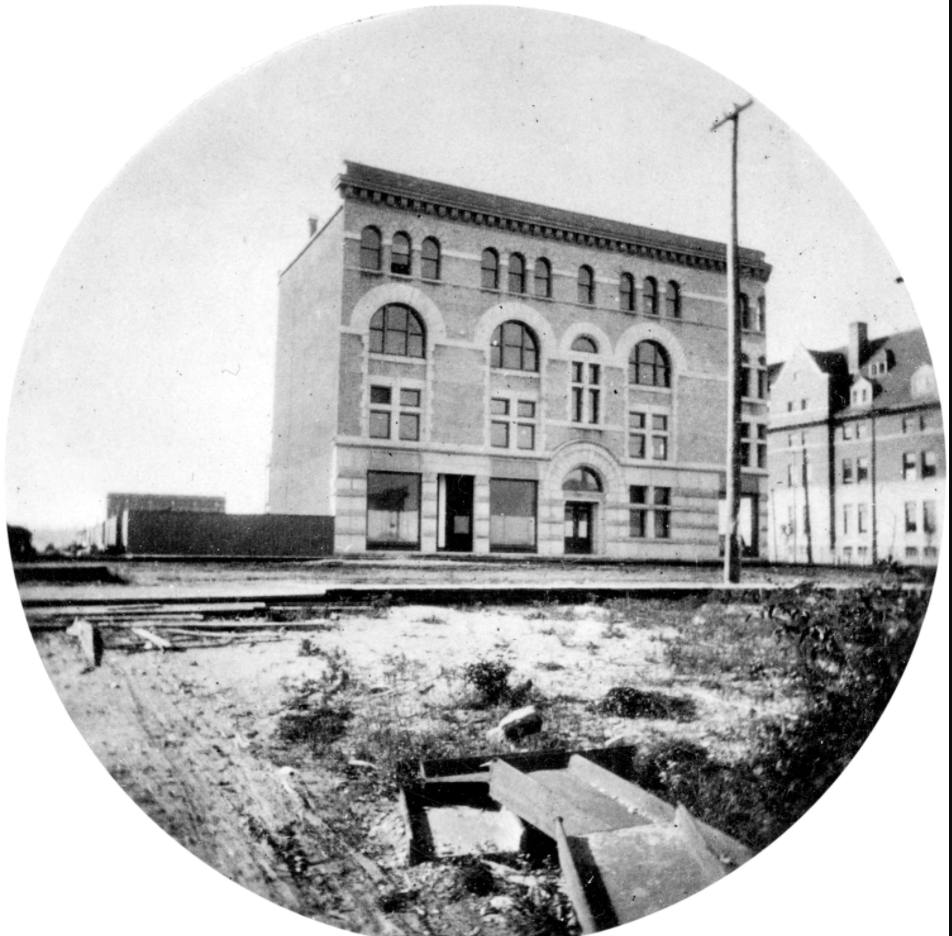
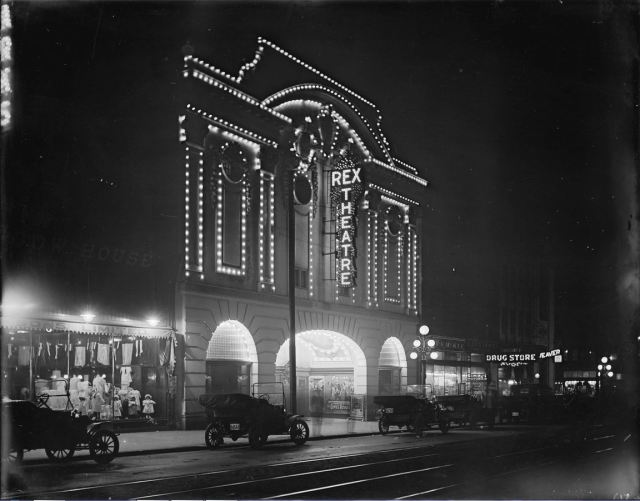
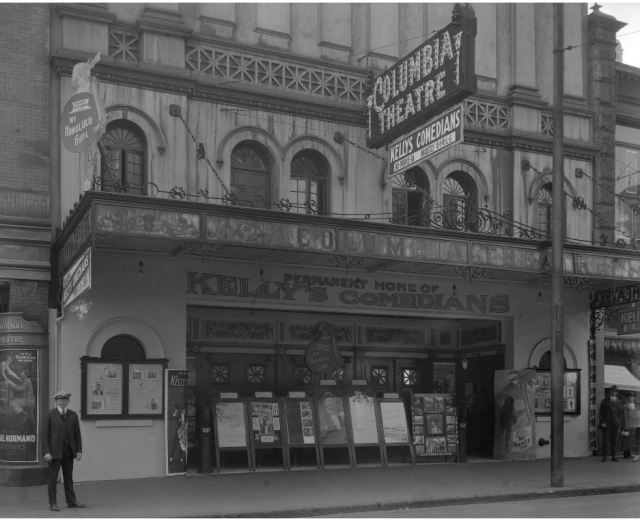
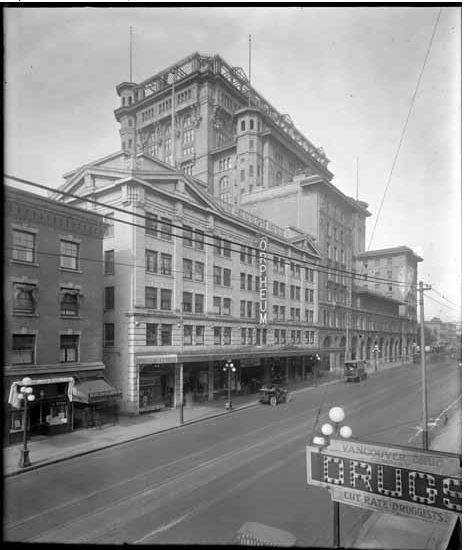
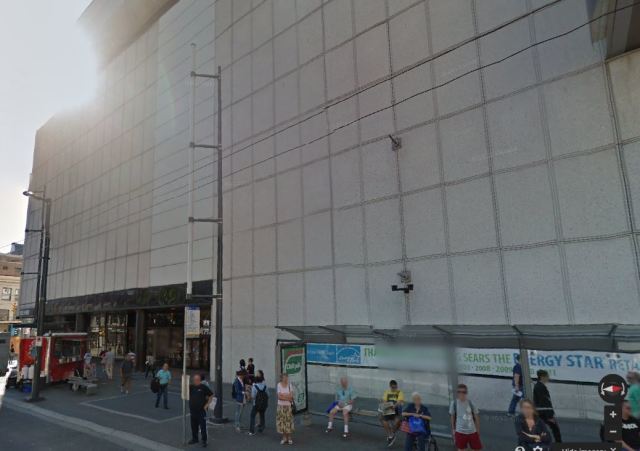
When the Pacific Centre took over Granville and Georgia Streets, it knocked out blocks of heritage buildings.
Story and photos from Vancouver Exposed: Searching for the City’s Hidden History

The Great White Urinal:
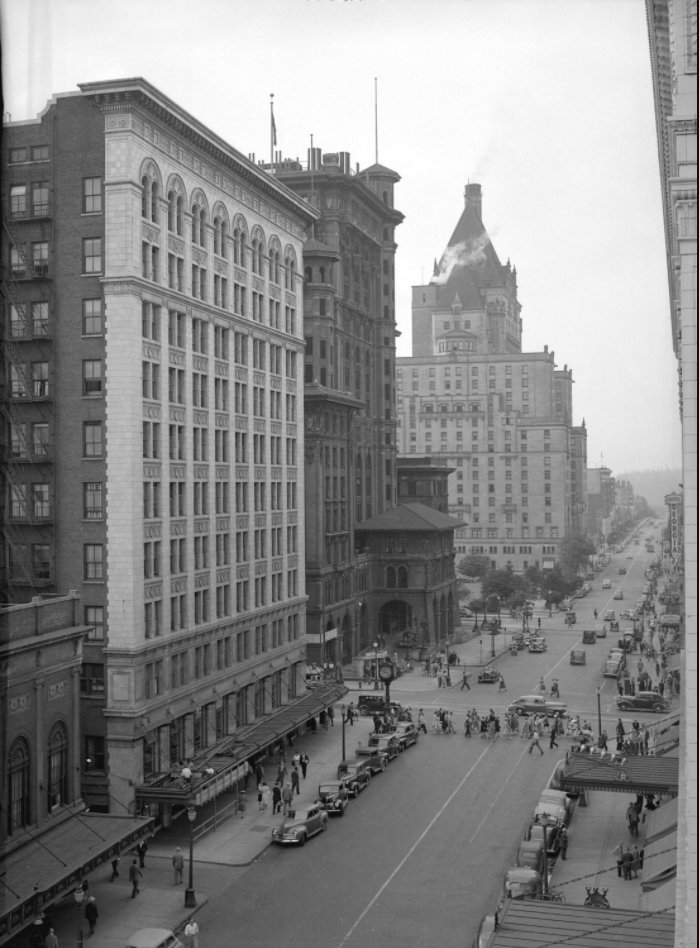
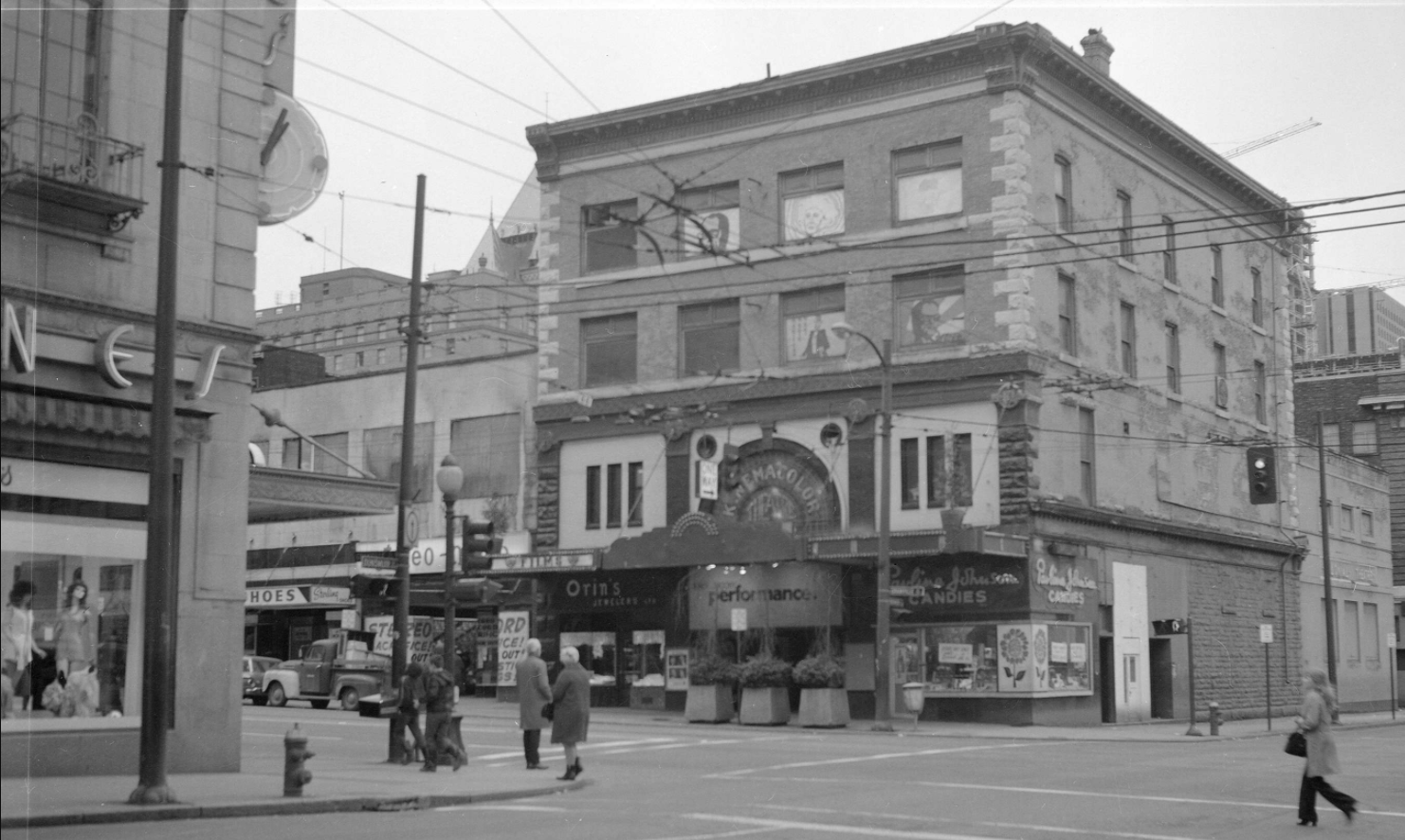
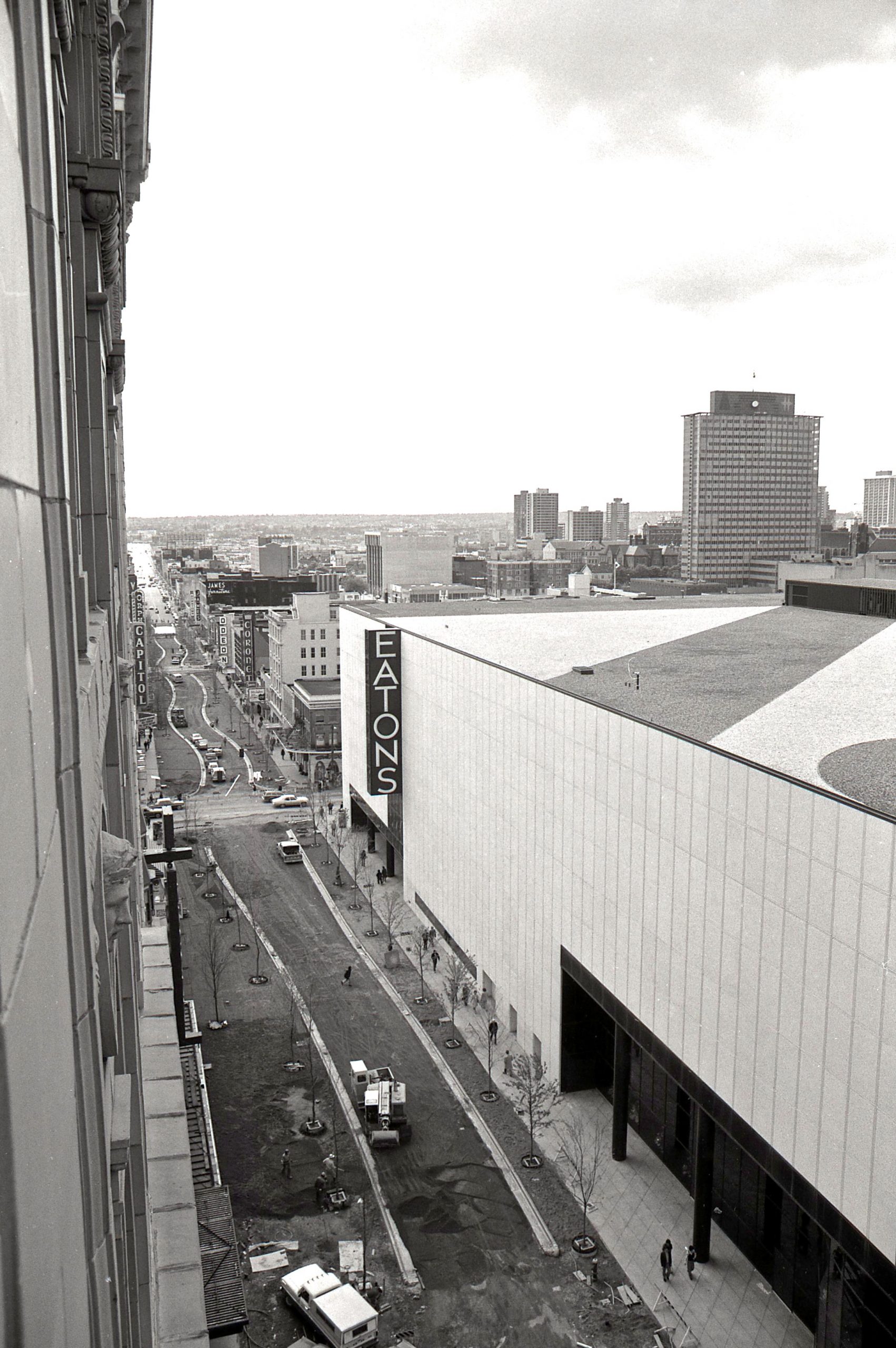
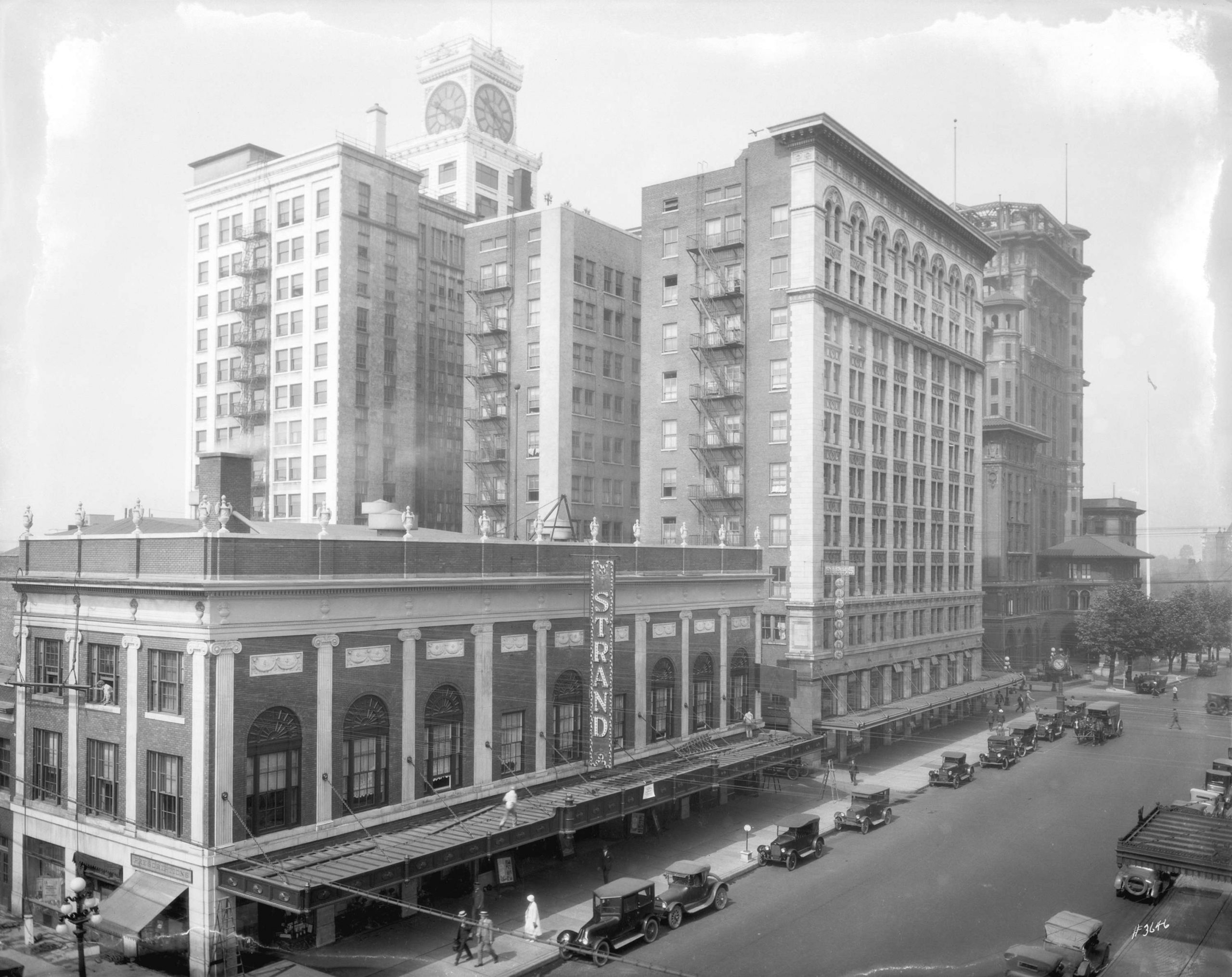
When I moved to Vancouver from Australia in the mid-1980s, locals had already had a dozen years to get used to Pacific Centre and the “Great White Urinal”—the name they’d not so affectionately dubbed the Eaton’s department store building. But it wasn’t until several years ago when I saw a 1924 photo showing the Strand Theatre, the Birks Building and the second Hotel Vancouver lined up along Georgia at Granville, that I realized how much we had lost.

In the 1960s, city council wanted a redevelopment of downtown Vancouver with Georgia and Granville Streets as the epicentre. The fear was that the downtown core would lose business to suburban malls and the hope was that a new, modern shopping centre would attract people and breathe life back into that intersection. The thought was that this retail vibrancy would come through a superblock and underground parking that spread across several blocks.

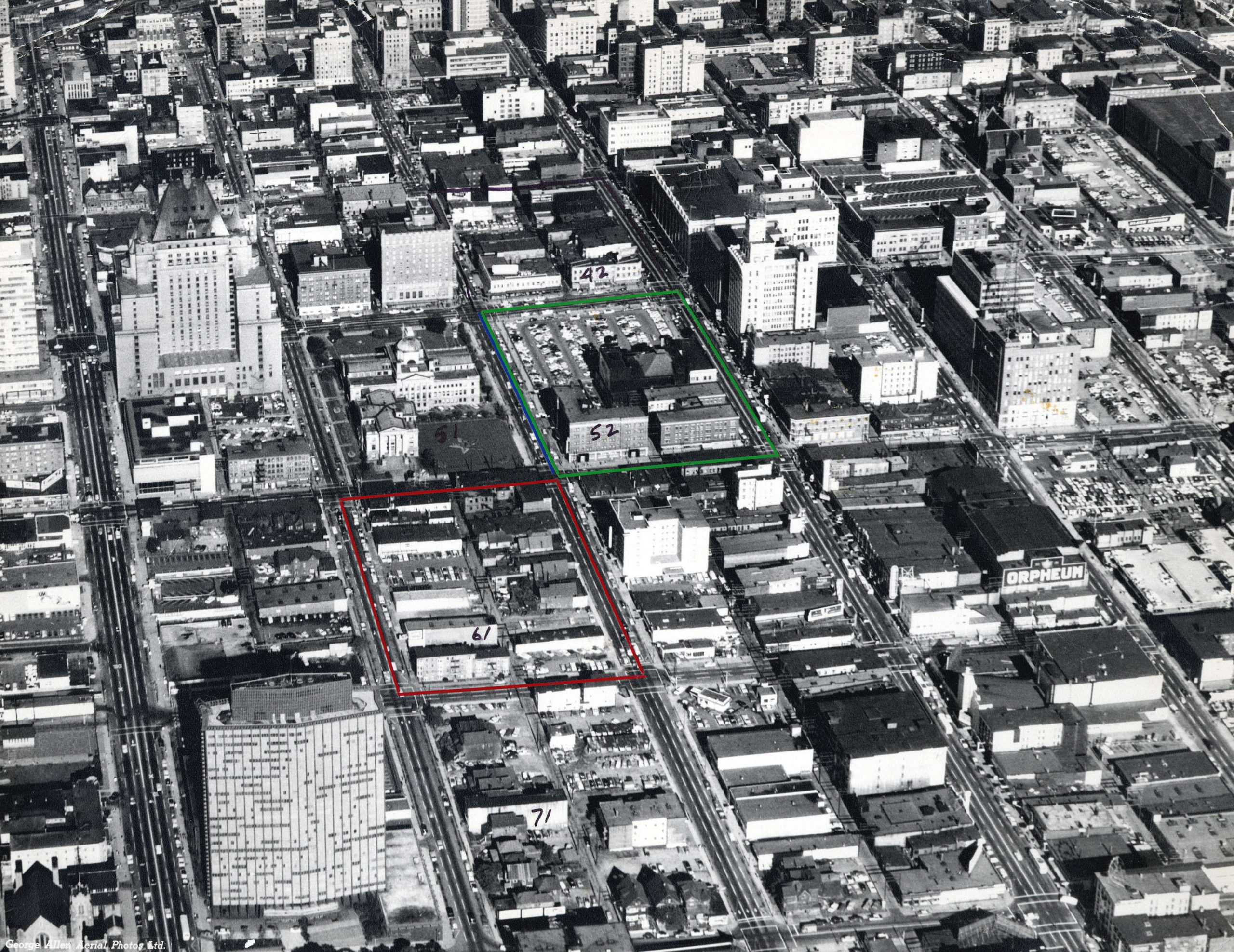
Superblock:
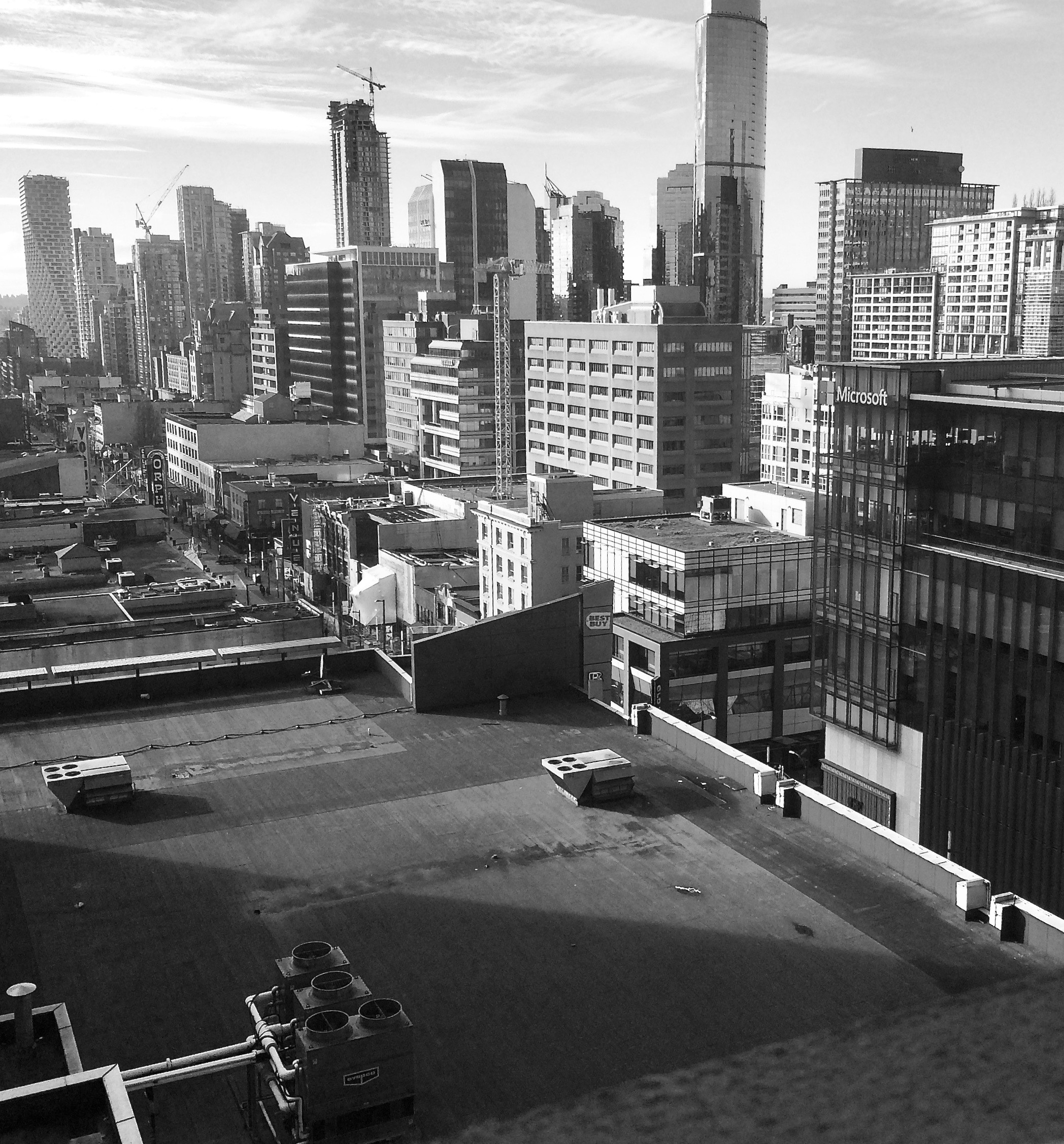
The superblock was made up of Block 52—bounded by Granville, Georgia, Howe and Robson; and Block 42—bounded by Granville, Georgia, Howe, and Dunsmuir. The problem was that the T. Eaton Company, which owned all of Block 52, wasn’t in a hurry to move from West Hastings (now SFU Harbour Centre) and a new department store was essential to anchor the proposed shopping mall.

The other problem was 18 individual landowners owned Block 42 and none of them wanted to sell. By the fifth redevelopment report in July 1964, a frustrated city council led by Mayor William Rathie were figuring out ways to expropriate their land.
Vancouver’s Greatest Day:
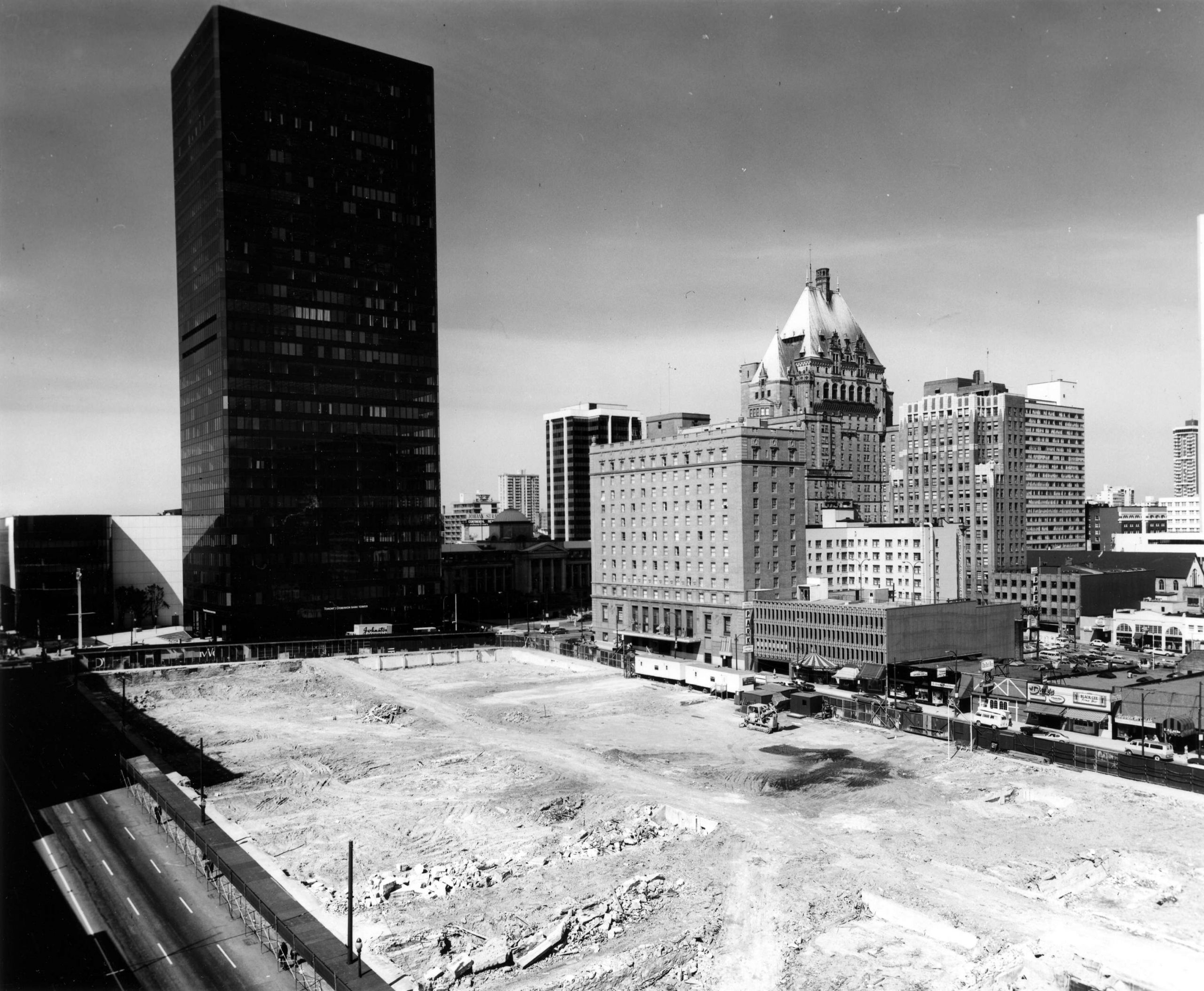
In May 1968, the city held a plebiscite to allow them to buy up all the properties in Block 42 and 70 percent of voters agreed. The next mayor, Tom Campbell, told the press: “We’ve got a united city which wants a heart. Vancouver had only a past—today it has a future. This is Vancouver’s greatest day.”

By 1974, we had the Pacific Centre and Vancouver Centre shopping malls, much of it as an underground bunker. We’d rid the streets of gorgeous brick buildings and gained the IBM tower, the former Four Seasons Hotel, the Scotia Tower and a 30-storey black glass monument to capitalism in the TD Tower. Rather than revitalize the Granville and Georgia intersection, we sucked the life right out of it.
Related:
The Second Hotel Vancouver: What were we thinking?
Vancouver’s missing heritage buildings
Vancouver Exposed: Searching for the City’s Hidden History
© All rights reserved. Unless otherwise indicated, all blog content copyright Eve Lazarus.














