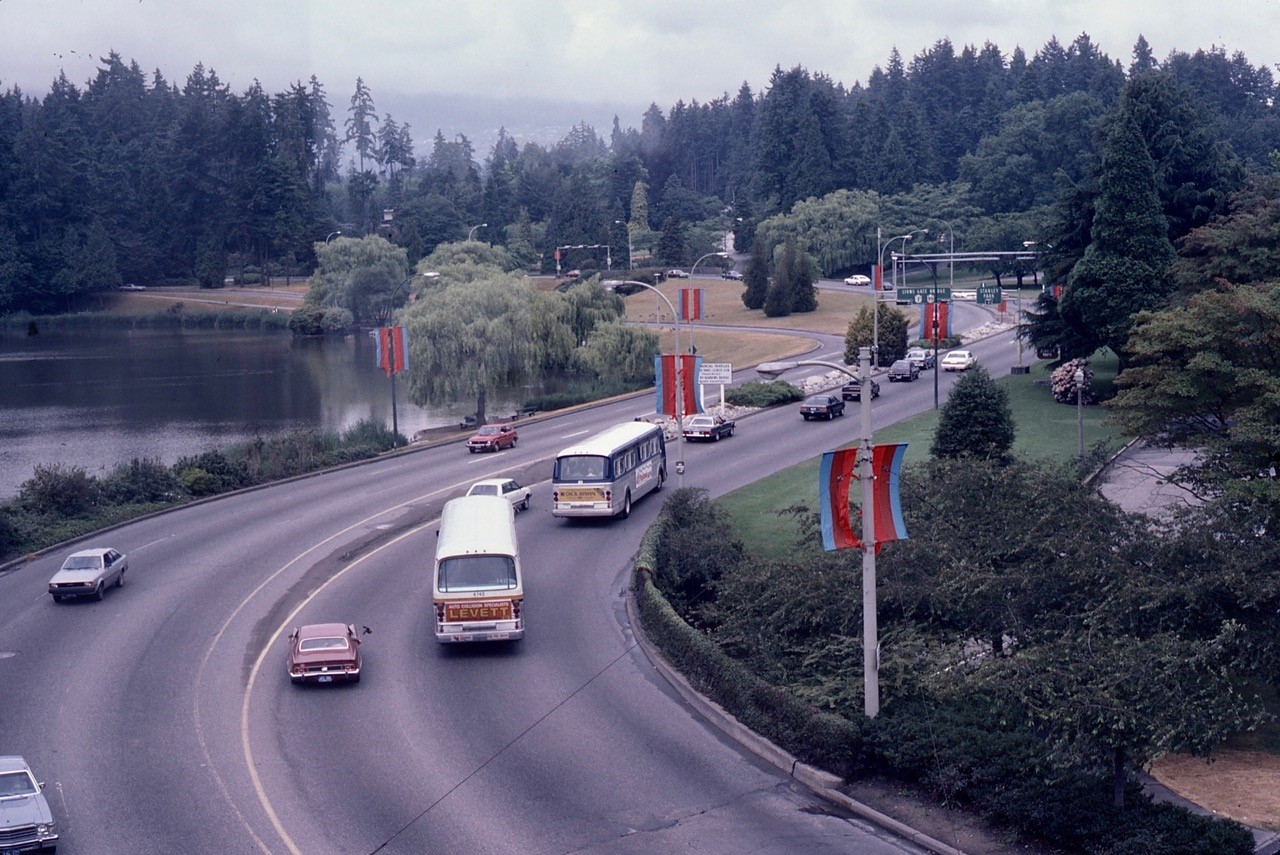
The name of the 11-acre green space at the entrance to Stanley Park known as Devonian Harbour Park has nothing to do with its indigenous history, the land’s connection to the Kanakas, the buildings that once dotted its landscape or Vancouver. The park was named after the Calgary-based Devonian Group of Charitable Foundations which forked over $600,000 to develop the site to its present look in 1983.
From Vancouver Exposed: Searching for the City’s Hidden History

Kanaka:
Kanaka was a term for indigenous Hawaiians who came to Canada in the early 1800s to work for the Hudson’s Bay Company’s fur trade. Most went home, but some stayed, married Squamish women and settled in Coal Harbour.
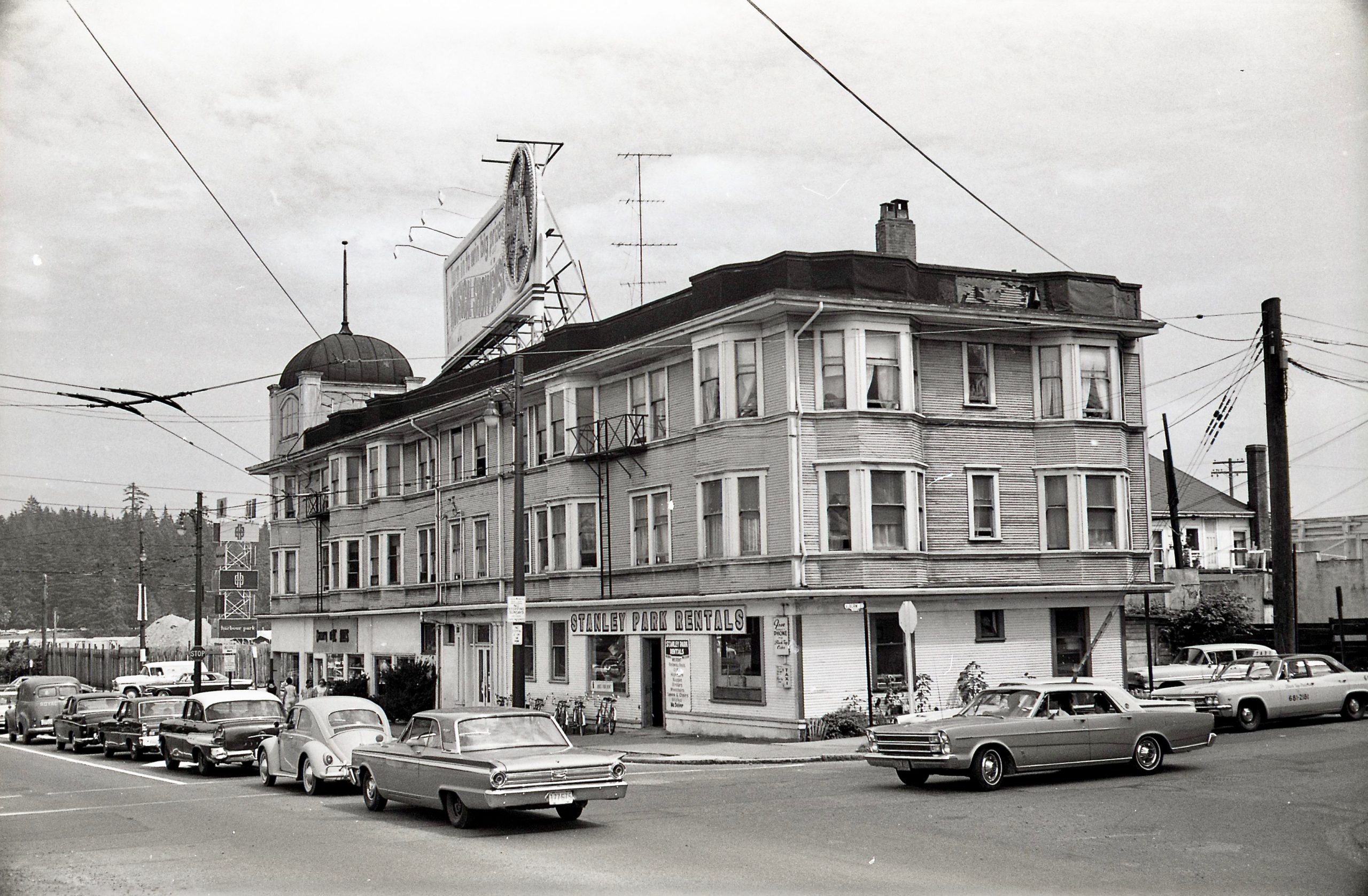
By the early 1900s, the Kanakas had been chased out and moved to the Mission Reserve in North Vancouver. That left the land free to develop. And, in 1911, Vancouver’s population of nearly 150,000 felt big enough to sustain a 10,000-seat arena. It was built by a couple of young guys from Victoria: brothers Frank and Lester Patrick (aged 25 and 27 respectively) who needed a home for their new Pacific Coast Hockey Association. As a comparison, Rogers Arena, built in 1995, has a capacity of 18,910.
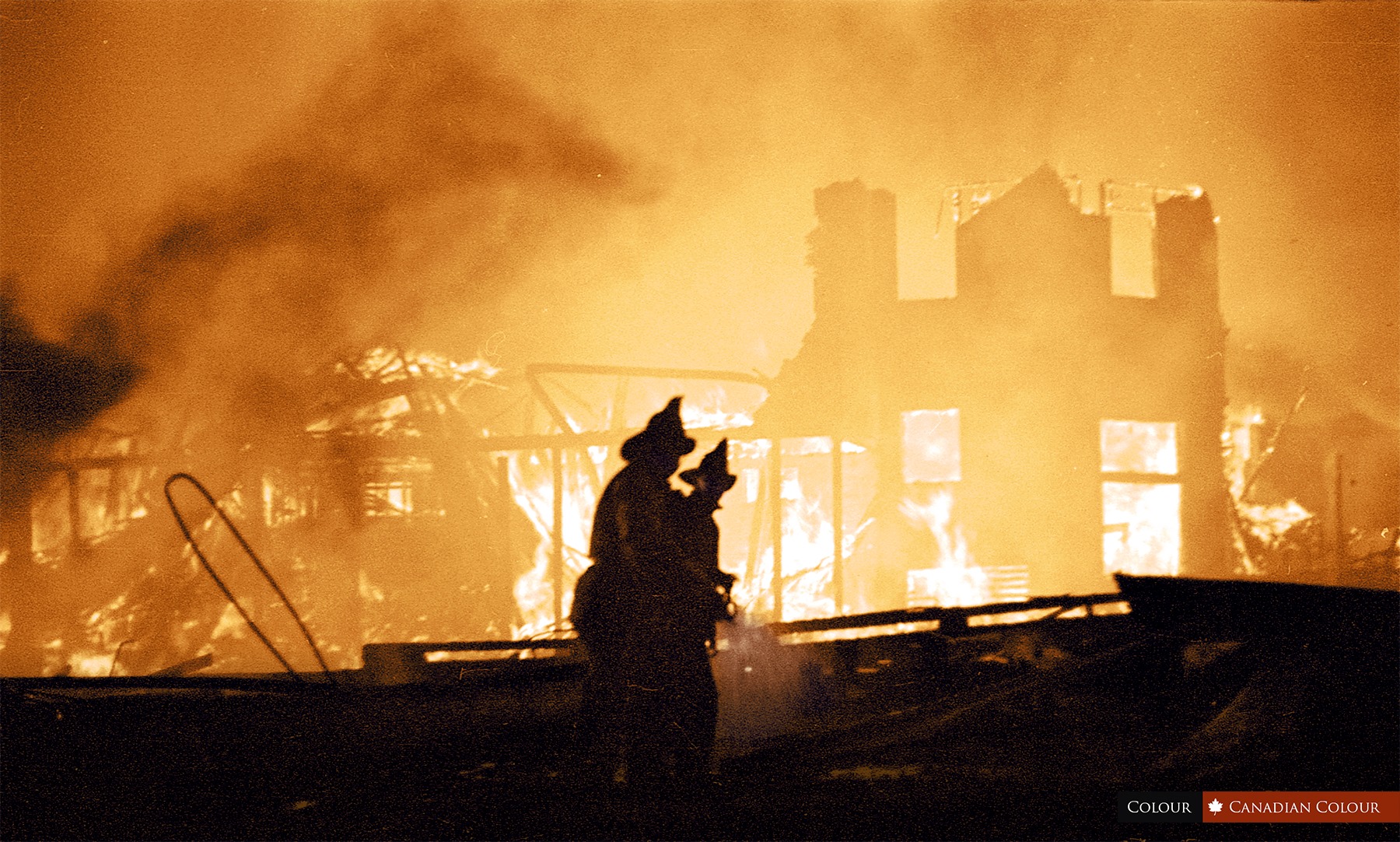

Denman Arena:
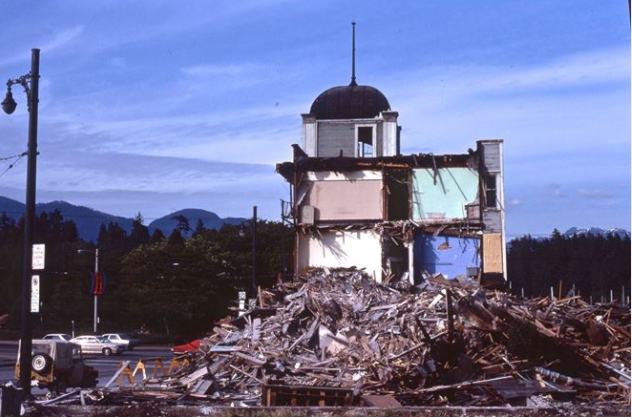
In 1915, the Denman Arena hosted Vancouver’s first and only Stanley Cup—when they beat the Ottawa Senators in three straight games. Rudolph Valentino judged a beauty contest, Arthur Conan Doyle (creator of Sherlock Holmes) gave a speech, and the arena was used for public skating, wrestling, military assemblies and musical performances.

Then on August 20, 1936, just hours after 4,000 boxing fans watched Max Baer fight James Walsh, the building burned to the ground.
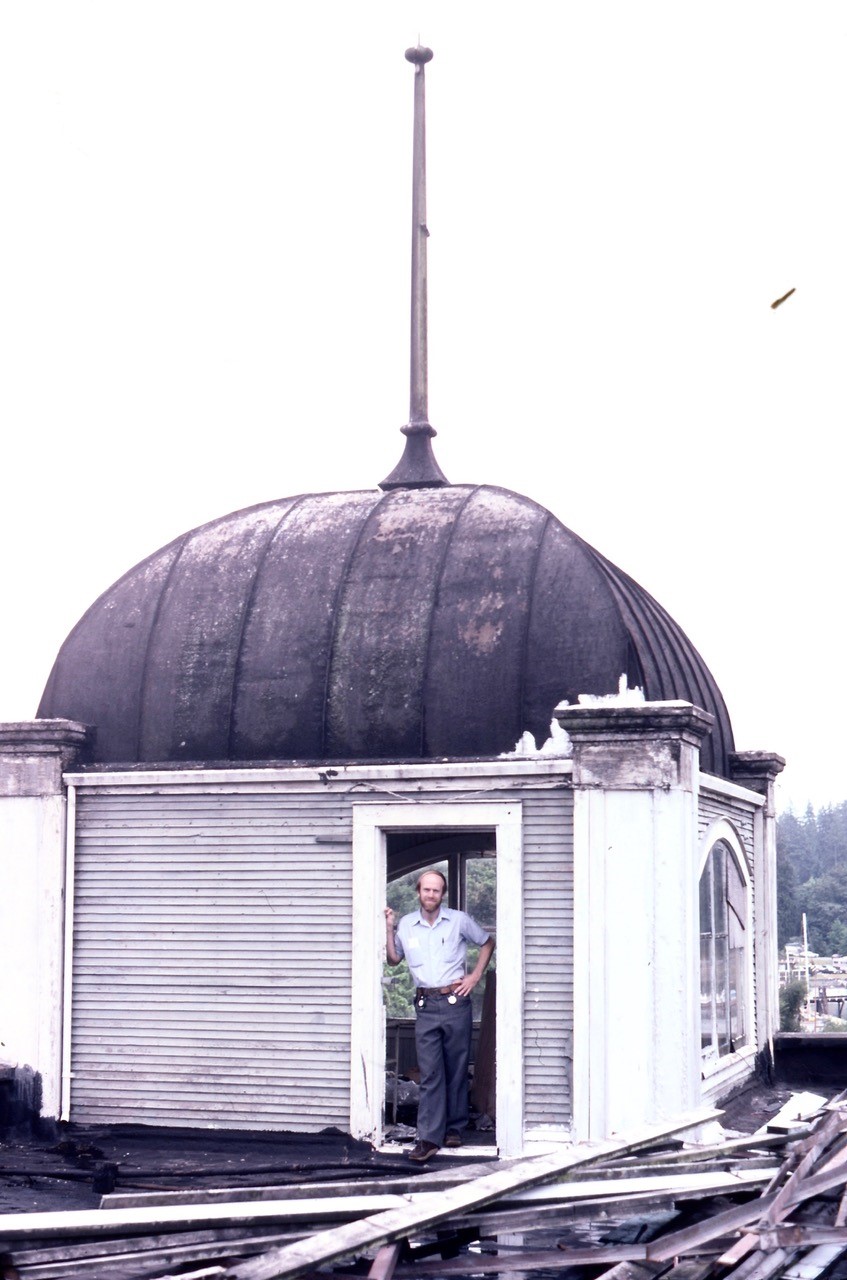
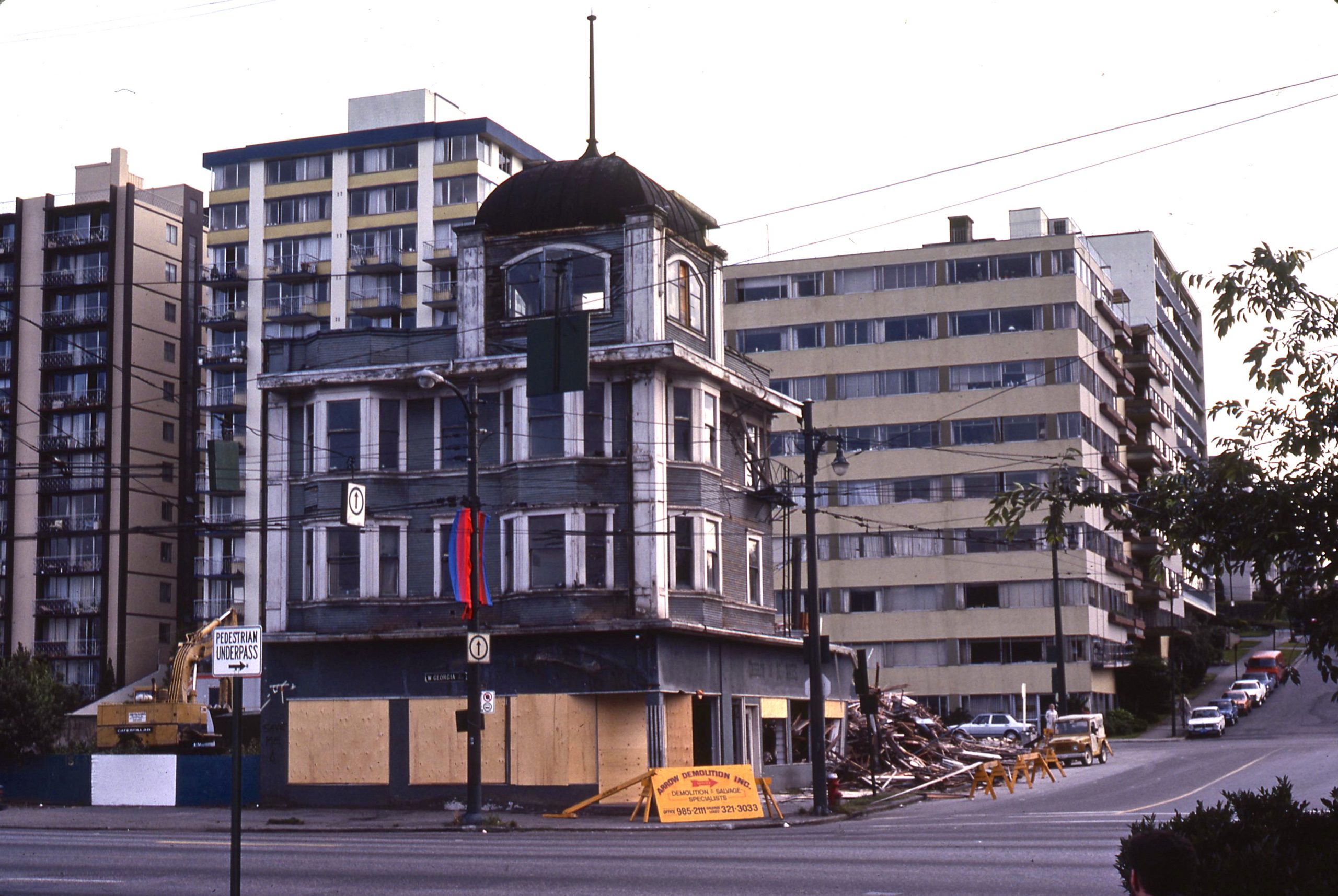
In 1927, the Patricks built the Denman Auditorium just to the south of the Denman Arena. The Auditorium survived the fire, went through a few different owners and names, hosted everything from political rallies to a strange assortment of revivalists and faith healers from the States.

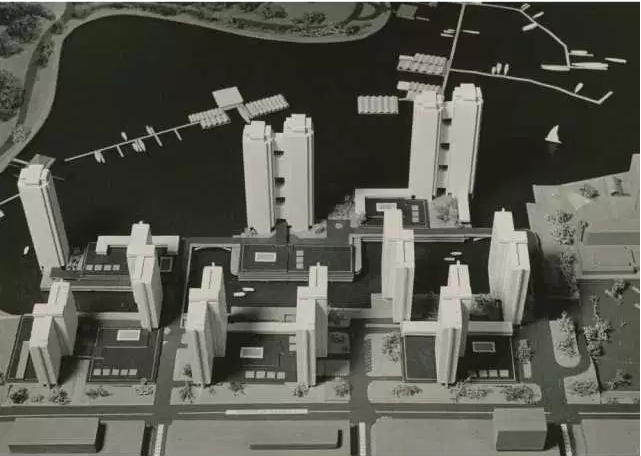
Development:
The building was demolished in 1959 to make way for the opening of the Queen Elizabeth Theatre.
Now devoid of buildings, developers dreamed of hotels and condos. The first attempt came from New York in the early 1960s. The second, by a local outfit called Harbour Park Developments that proposed 15 towers soaring up to 31-storeys in height. The third was a plan by the Four Seasons Hotel chain. They wanted to build a 14-storey hotel, three 30-storey condos towers, and a bunch of townhouses.
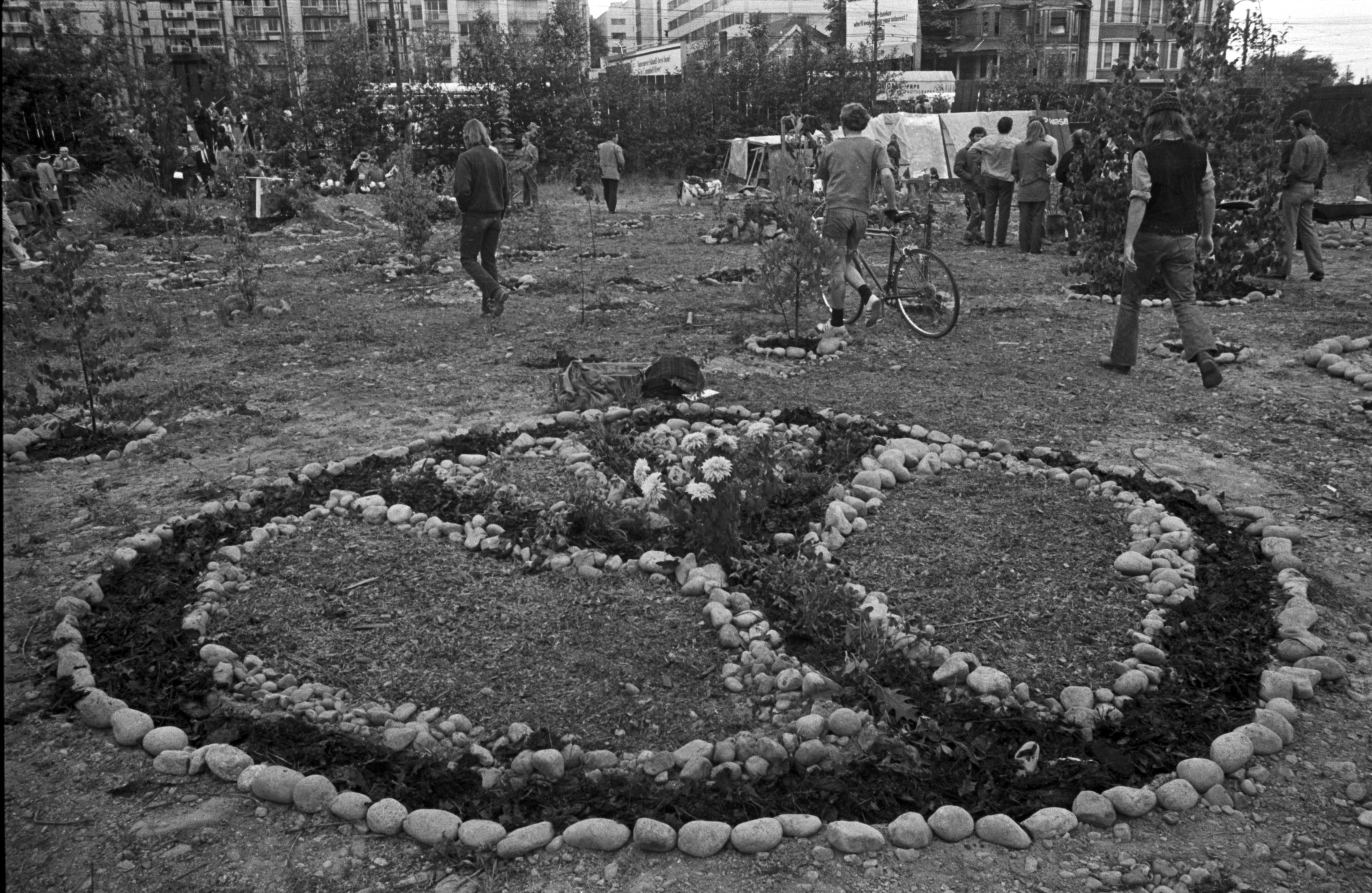
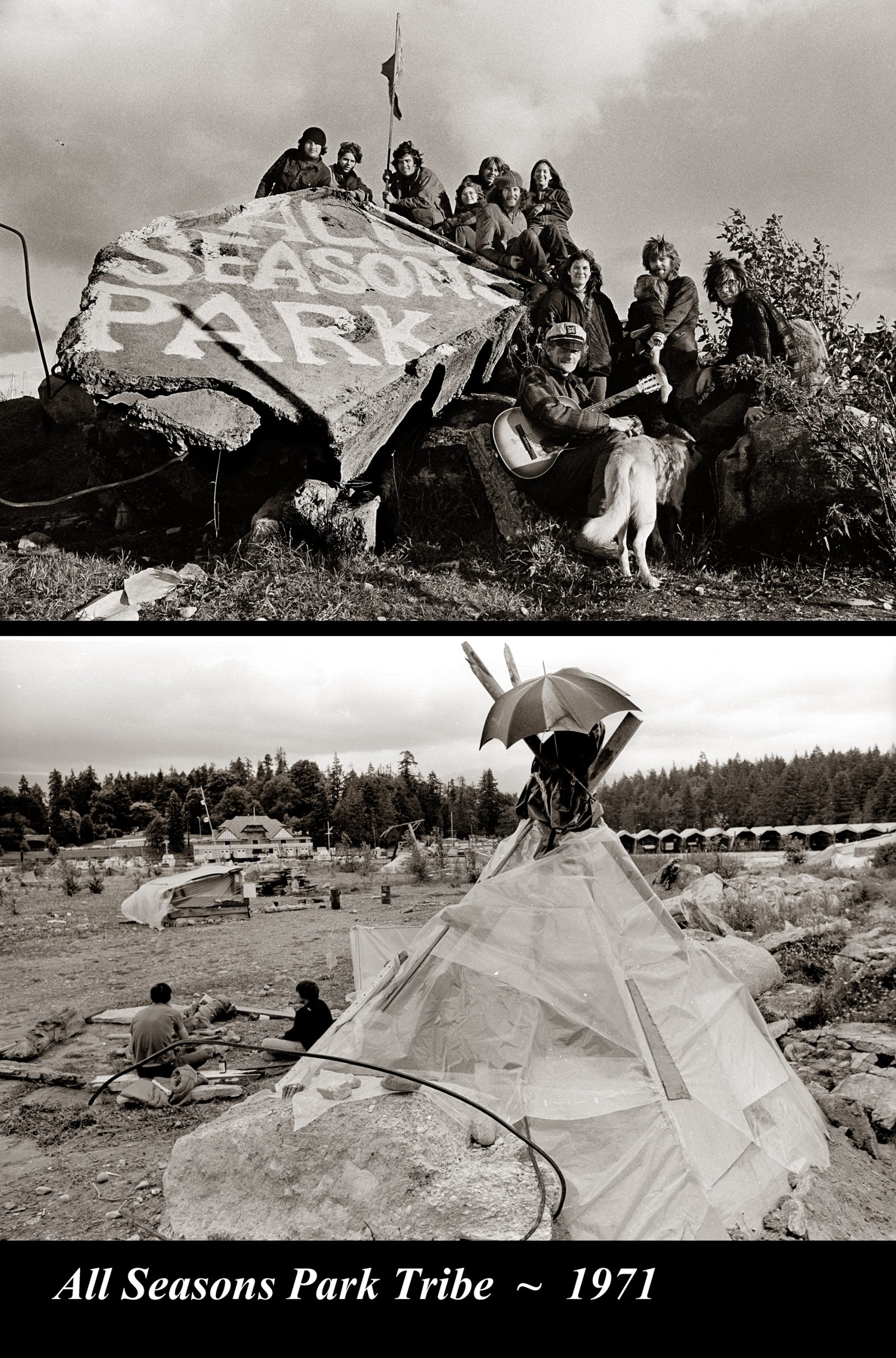
Hippies:
On May 29, 1971 about a hundred hippie/activists took over the site. They planted maple trees and vegetables, dug a pond, and installed children’s playground equipment. They called it All Seasons Park. The hippies lasted just under a year. Mayor Tom Campbell brought in the backhoes and knocked all the shelters down. Campbell’s own development dream fell apart later that year when the Federal government refused to hand over a crucial piece of land. Instead, the land was annexed to Stanley Park and purchased by the City of Vancouver.

© All rights reserved. Unless otherwise indicated, all blog content copyright Eve Lazarus