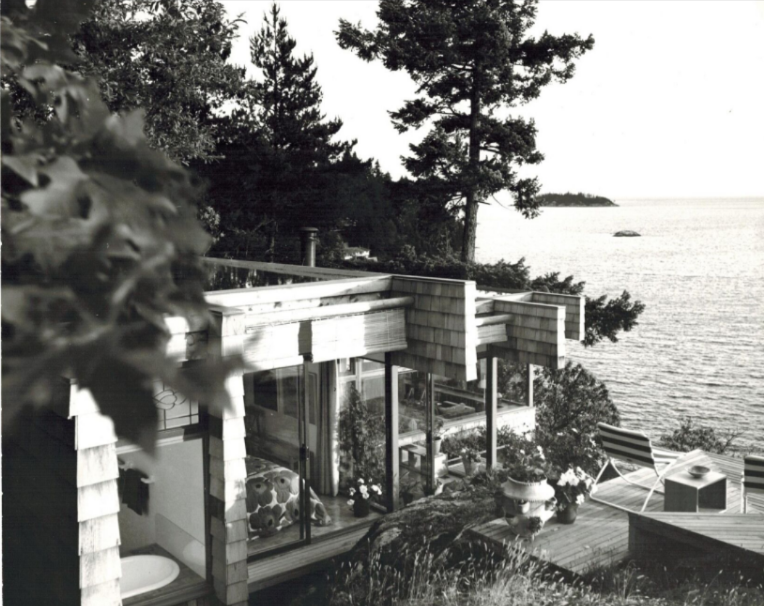
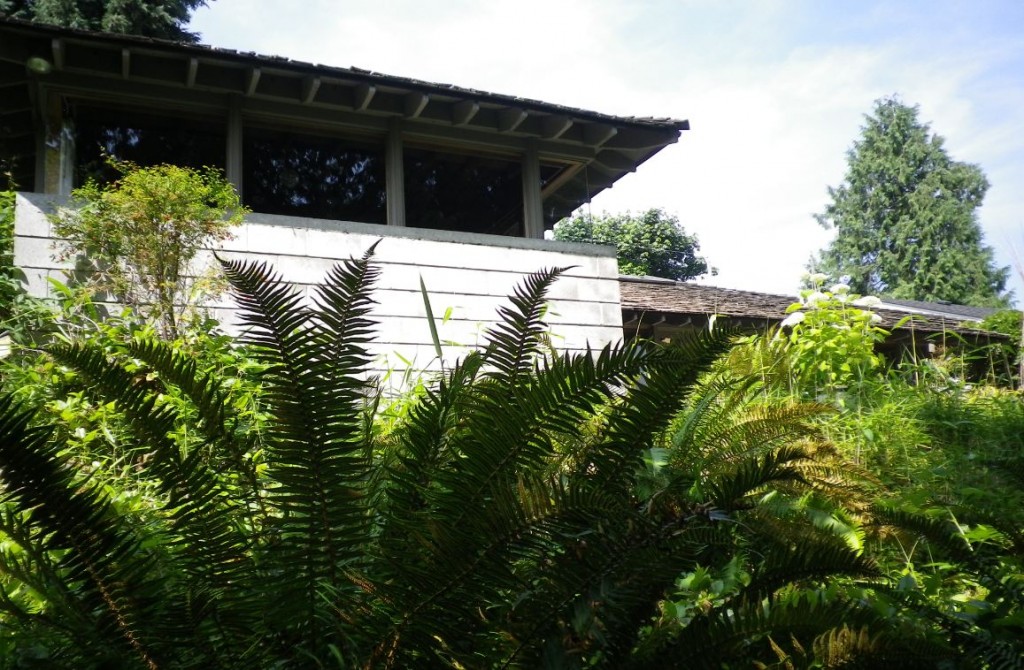
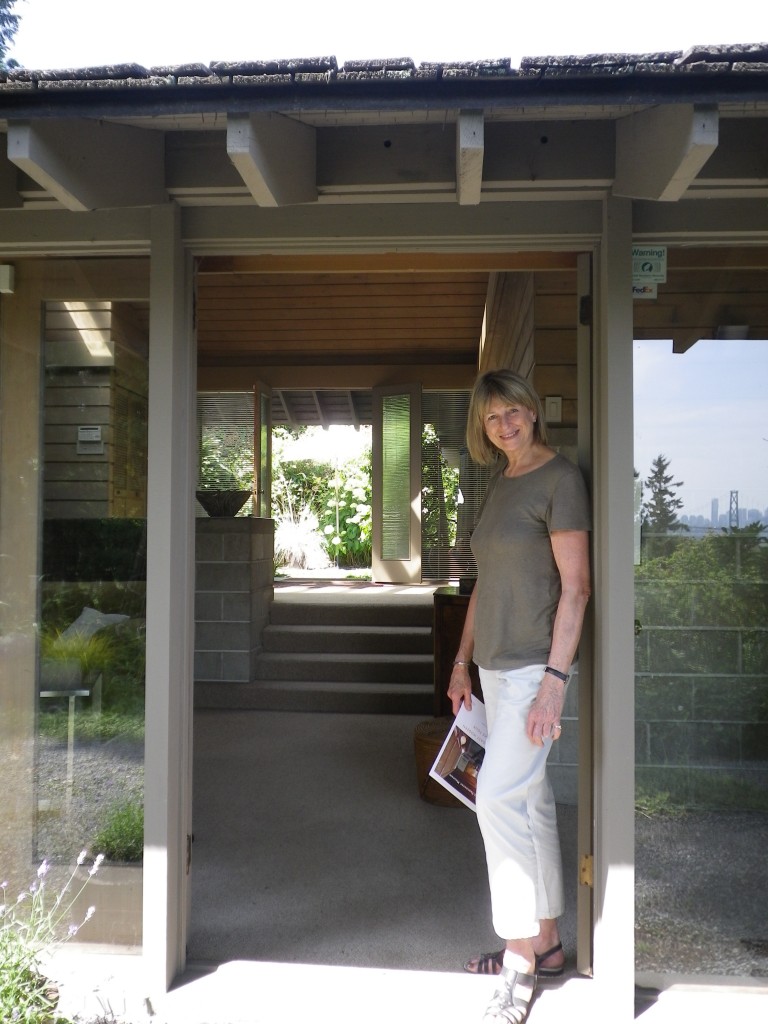
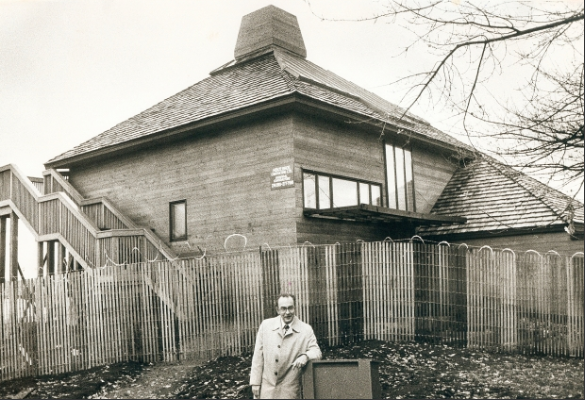
Architect Ron Thom designed a 4,000 sq.ft. prize home for the PNE in 1981. It resided in South Surrey.
In 1981, British Columbia was in the throes of a recession, house prices were plummeting, and first-time buyers were looking at interest rates of over 20%.
Architectural offices were closing, and even a starchitect like Ron Thom was searching for clients. So, a commission to design the PNE prize home likely would have been very welcome.

West Coast Modern:
Thom had cut his teeth designing more than 60 mid-century modern homes mostly on the North Shore, but had moved onto work on commercial buildings such as the BC Electric Building in Vancouver, and after he opened an office in Toronto, designed the Massey College, the Shaw Festival Theatre and the Toronto Zoo.
For the PNE, he designed a bright and airy home of close to 4,000 square feet—more than twice the size of earlier prize homes. Behind the solid oak front door was a dramatic glass-roofed atrium which soared up from the courtyard entrance to the roof. Short flights of stairs led to the living areas, a self-contained master bedroom was placed at the top of the house and four bedrooms below. It was likely frightening for people used to traditional houses with small rooms, two floors and a basement.
Financial Problems:
It was also quite complex and costly to build on top of the cost of the Coquitlam lot which had been purchased as its designated resting place.
Batex Industries, the builder, ran into financial trouble and liens were placed on the house by several contractors, and by Thom.
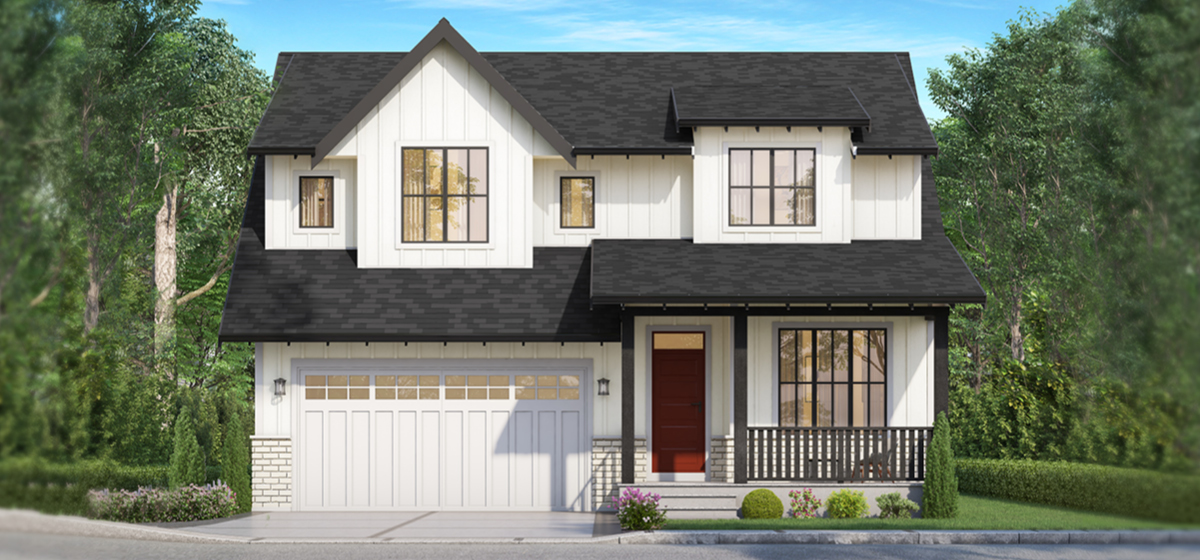
PNE staff thought it too modern for the average family, and according to a Vancouver Sun story, the winners took the $250,000 cash option and stayed in North Vancouver. Ron Thom’s PNE house eventually sold for $2,500 and shipped to a lot in South Surrey. It was replaced in 2015 by a glaringly modern two-storey home in 2015.
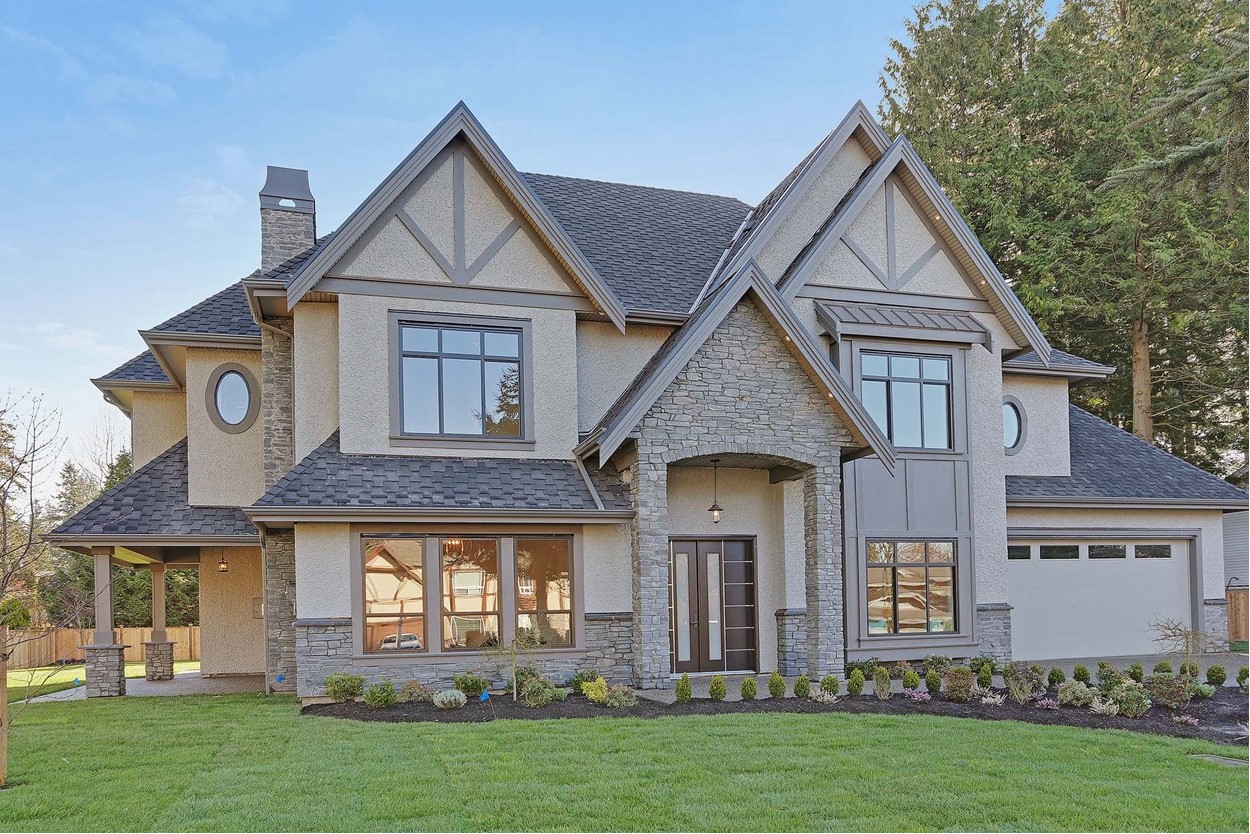

This year’s PNE house is a 3,400 sq-foot, three-bedroom house in Langley. Need more bedrooms? No worries. The main bathroom will divide into at a couple more and you can Air B&B out the media room.

For more information about Ron Thom and other mid-century modern architects, check out Sensational Vancouver. And, for more stories like this one see: Vancouver Exposed: Searching for the City’s Hidden History
Related:
© All rights reserved. Unless otherwise indicated, all blog content copyright Eve Lazarus.
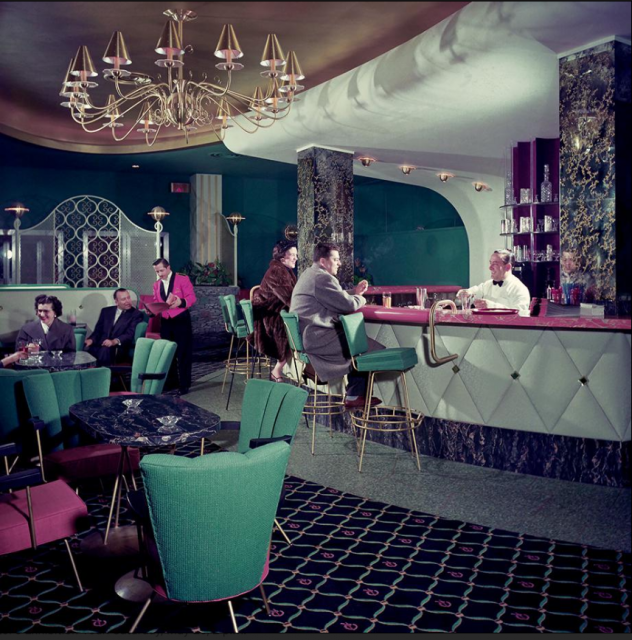
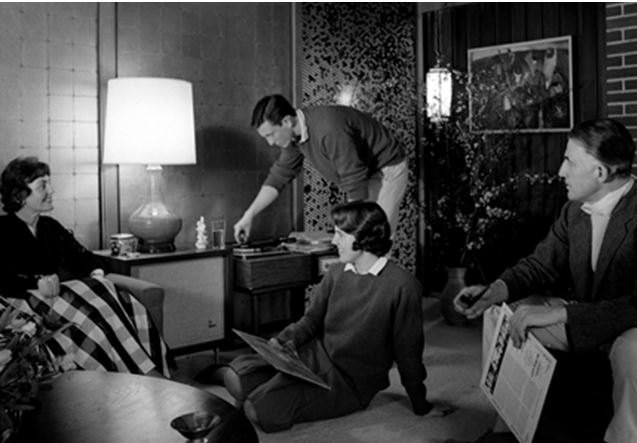


















 Erickson and
Erickson and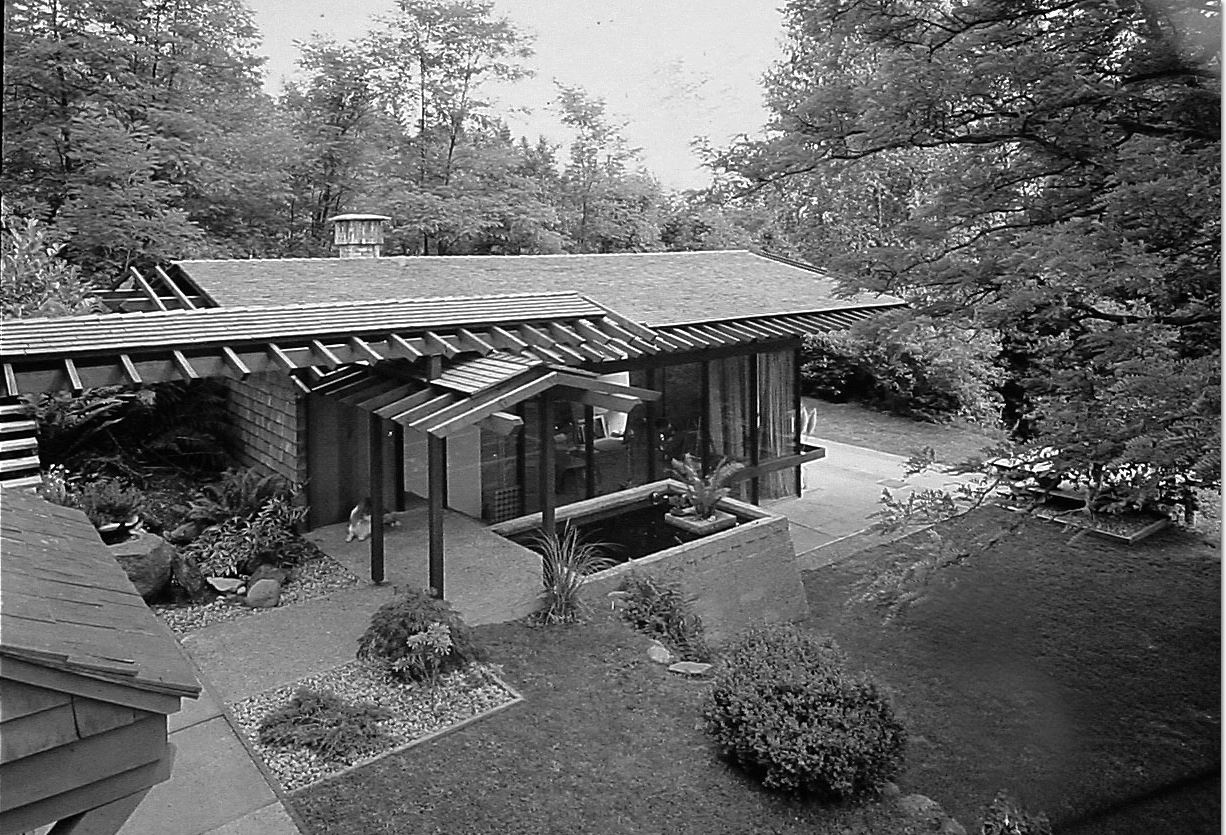 
 Cover image by
Cover image by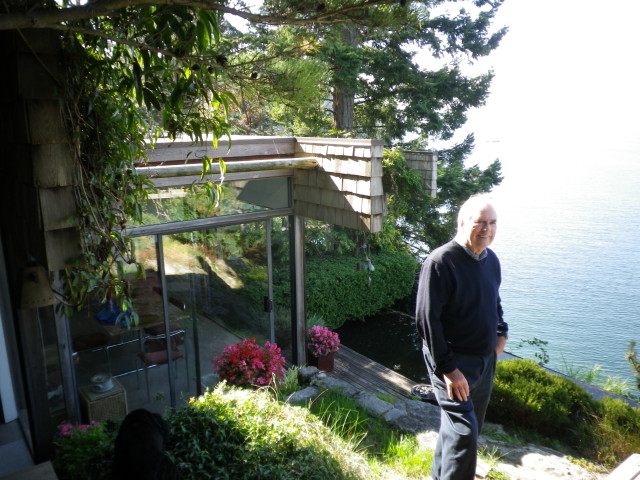 
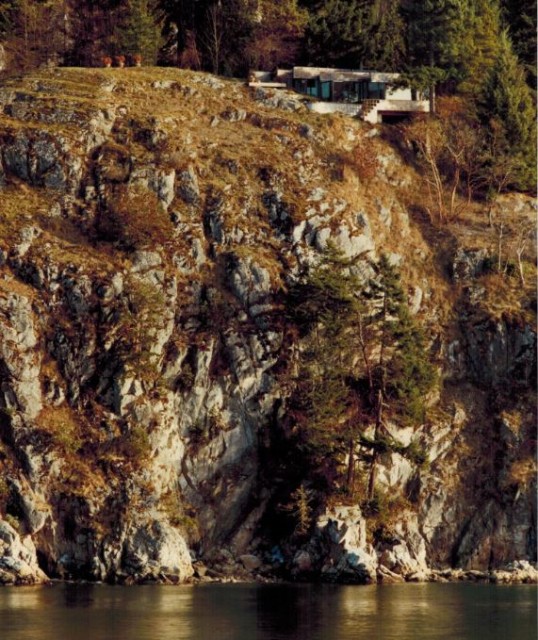 Rapidly disappearing:
Rapidly disappearing:







